Template overview
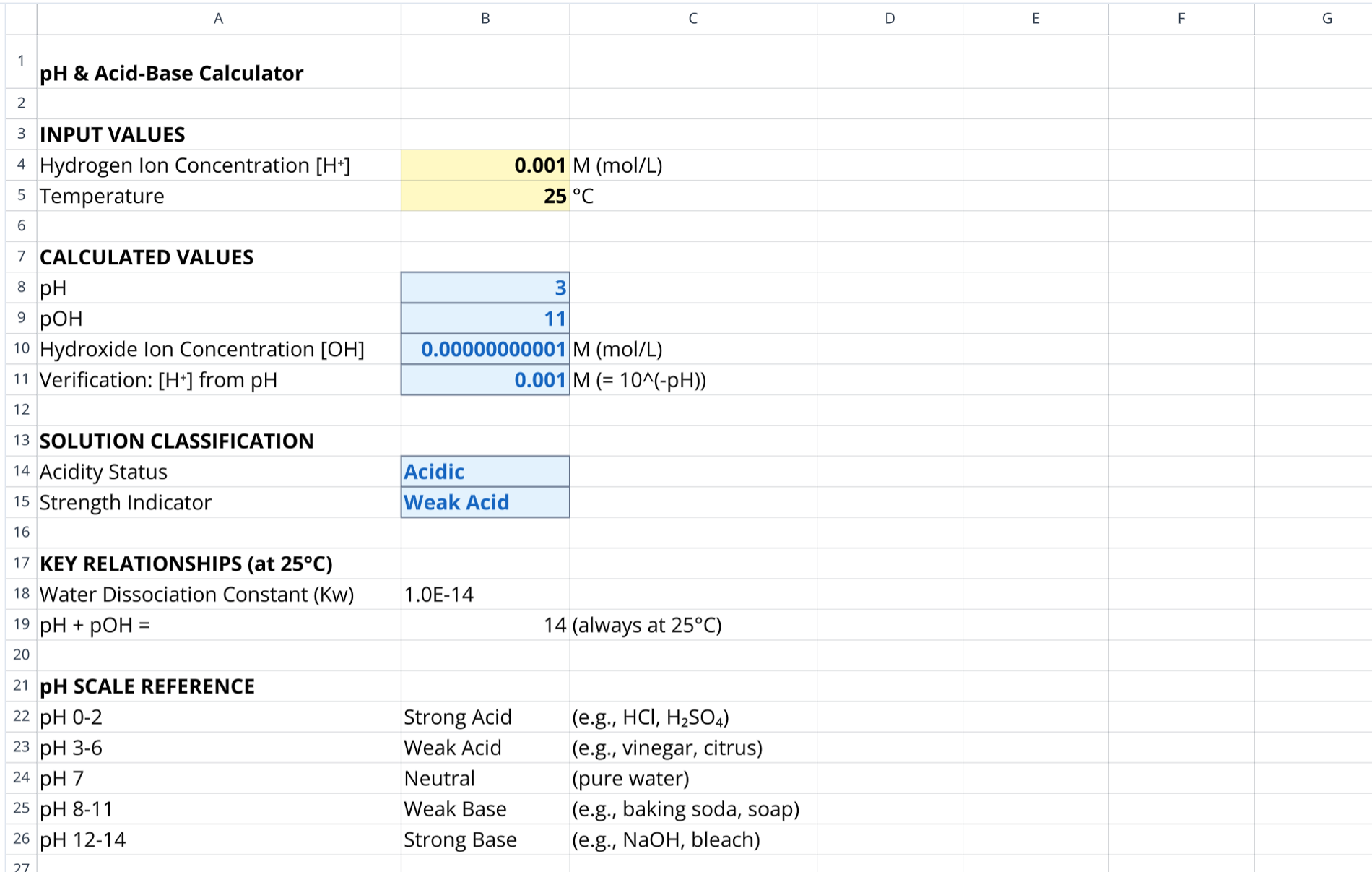
This single-sheet tool, much like a quadratic formula calculator, is designed to calculate pH levels directly from hydrogen ion concentration. It operates entirely using standard spreadsheet formulas, distinguishing it from a coding spreadsheet that might require external scripts or Python code.
The template provides instant conversion between acidity, basicity, and ion concentrations. It also includes built-in reference tables for acid-base classification to provide immediate context for the calculated results.
Input parameters
The template relies on specific inputs located in the top section of the sheet to drive the calculations.
- Hydrogen ion concentration: This is the primary user input field. It accepts values in Molar (M) units (currently set to 0.001 M by default).
- Temperature: A contextual input set to 25°C is included to validate the standard constants used in the formulas.
- Data flow: The sheet follows a unidirectional flow, moving data from the input cells in column B to the calculated results immediately below.
Automated outputs and logic
Primary calculated values
The calculated values section (rows 8-11) displays the derived quantities based on the user inputs.
- pH output: Displays the resulting pH value calculation derived from the input concentration.
- pOH derivation: Shows the corresponding pOH value based on the standard 14-point scale.
- Hydroxide ions: Calculates the $[OH^-]$ concentration using the water dissociation constant.
- Verification: Performs a reverse calculation to regenerate the hydrogen ion concentration from the computed pH, ensuring mathematical accuracy.
Underlying formulas
The template uses standard acid-base chemistry equations, which can also be assisted by an AI formula generator, to generate results.
- Logarithmic conversion: Demonstrates how to calculate pH using the negative base-10 logarithm of hydrogen ions.
- pOH relationship: Applies the formula $14 - pH$ to determine alkalinity, assuming standard temperature conditions.
- Dissociation constant: Uses $Kw$ ($1.0 \times 10^{-14}$) to solve for hydroxide concentration.
Reference data and visual aids
To support the calculations, the template includes reference sections that map numerical values to chemical concepts.
- Constants section: Lists fixed values for $Kw$ and the pH-pOH relationship at standard temperature.
- Classification table: Maps specific pH ranges to categories, such as Strong Acid, Weak Base, or Neutral.
- Real-world examples: Provides common substance examples corresponding to calculated ranges to aid in understanding.
- Formula documentation: Explicitly lists the math used to calculate pH and pOH for educational transparency.
Who this pH calculator is for
- Chemistry students: For verifying homework answers and understanding the relationship between hydrogen and hydroxide ions.
- Laboratory technicians: For performing quick bench calculations when preparing standard solutions.
- Educators: For demonstrating the mathematical mechanics of acid-base chemistry without relying on complex software or manual calculations, though Quadratic also functions as a python spreadsheet for more advanced computations.
Use Quadratic to calculate pH levels
- Calculate pH directly from hydrogen ion concentration using standard spreadsheet formulas.
- Instantly convert between acidity, basicity, and various ion concentrations.
- Leverage built-in reference tables for acid-base classification and real-world examples.
- Verify pH and pOH calculations with reverse derivations for mathematical accuracy.
- Understand the underlying logarithmic conversions and dissociation constants through explicit formula documentation.
- Quickly perform bench calculations or verify homework answers without complex software.