Table of contents
- Why standard SEO spreadsheets fail at scale
- Step 1: Importing and structuring your SEO data
- Step 2: Merging data with Python (no more VLOOKUPs)
- Step 3: Visualizing and updating in batches
- Step 4: Validating character counts and completeness
- Conclusion: From spreadsheet to CMS
- Use Quadratic to batch update SEO meta tags
Every SEO manager knows the specific anxiety of preparing a bulk upload file for a large website. You have a master list of five thousand URLs, and you have a separate document containing new, optimized titles and descriptions. Your task sounds simple: map the new content to the old URLs and generate a clean CSV for your CMS.
However, in traditional spreadsheets, this is rarely simple. You rely on fragile VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP formulas that break if a column is sorted incorrectly, and studies show a high percentage of spreadsheets contain errors. You struggle to visualize which sections of the site are complete because everything is trapped in endless rows. While many people search for an seo meta tag generator looking for a tool to write the copy for them, the bigger challenge is often the logistics of managing the data itself.
Quadratic offers a different approach. By combining the familiarity of a spreadsheet with the power of Python, essentially a python spreadsheet, and an infinite canvas, you can build a robust, crash-proof system to merge, validate, and batch-update your metadata. This article outlines how to move beyond manual cell dragging and build a reliable bulk management workflow.
Why standard SEO spreadsheets fail at scale
The traditional "SEO Audit Template" works well for small sites or one-off checks. However, when you are managing an enterprise e-commerce site or a large publisher domain, where effective product catalog management is essential, and considering the unique enterprise SEO challenges, standard spreadsheets begin to crumble under the weight of the data.
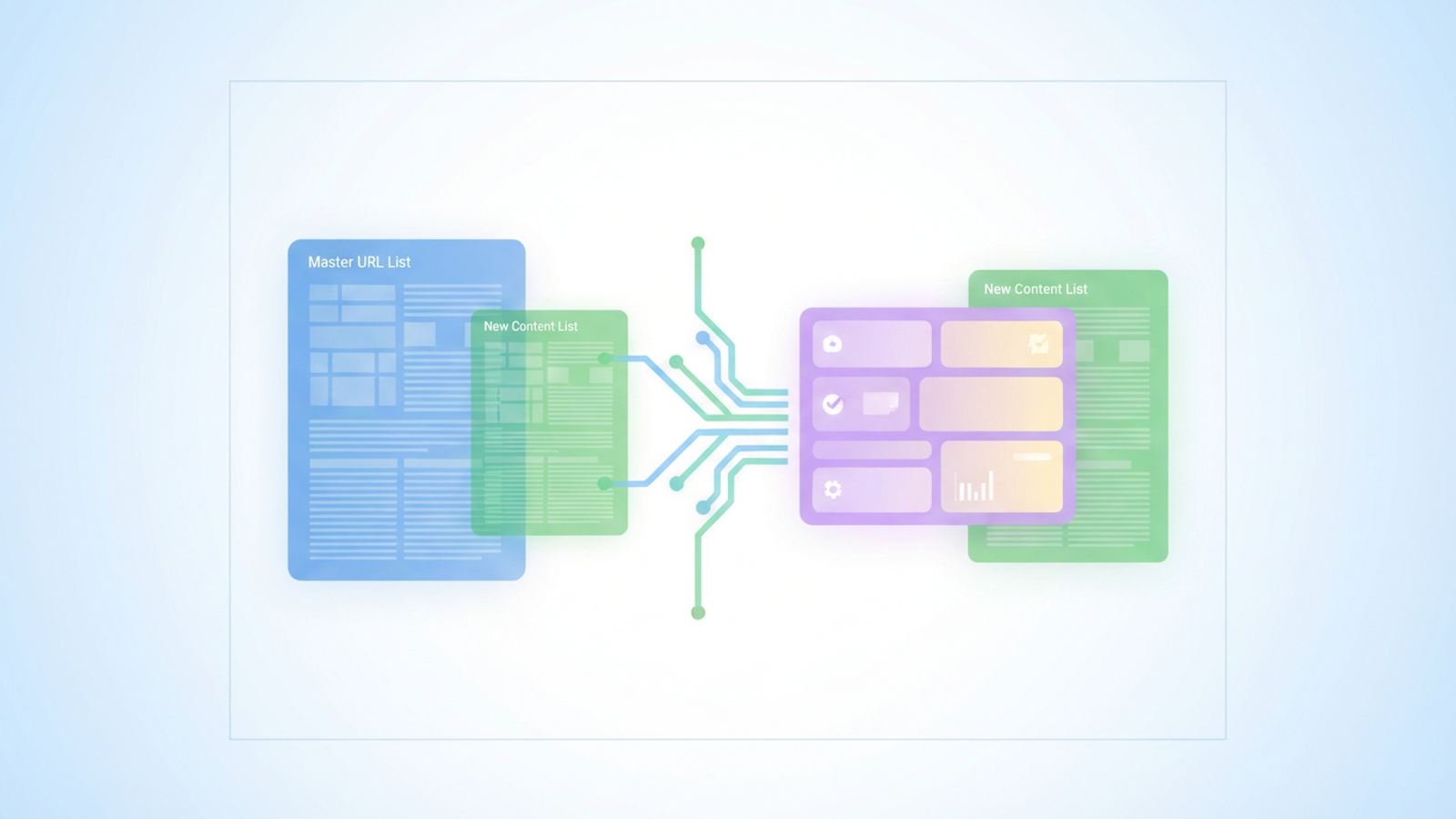
The most common point of failure is the enrichment process. You usually start with a "Master URL List" exported from a crawler like Screaming Frog, and you need to merge it with a "New Content List" created by your copywriters. In Excel or Google Sheets, you might use VLOOKUP to match these datasets. If one row shifts or a formula isn't dragged down all the way to row 5,000, you risk overwriting the wrong data. A title meant for a raincoat product page could end up on a shoe product page, creating a disaster for your click-through rates.
Furthermore, standard sheets lack visual organization. To manage different batches of updates—like the "Summer Collection" versus the "Blog Archive"—you are forced to use hidden rows or separate tabs, making it difficult to see the full scope of your project. While a tool like the meta tag generator seo moz offers is excellent for researching individual keywords or checking a single page, it does not solve this implementation workflow. There is a better way to generate your bulk upload files using Python.
Step 1: Importing and structuring your SEO data
The first step in your new workflow is bringing your data into Quadratic. Unlike a standard spreadsheet that forces all data into a single grid, Quadratic utilizes an infinite canvas. This allows you to import your distinct datasets and place them side-by-side visually, rather than hiding them in different tabs.
You will likely have two primary data sources. First is your Master Dataset, which contains your live URLs, current status codes, and unique IDs. Second is your Enrichment Dataset, which contains the new Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, and H1s you have prepared.
In Quadratic, you can pull these in as CSVs or connect directly to your database. By placing the Master list on the left and the Enrichment list on the right, you can visually inspect the structure of both files before you attempt to merge them. This setup is the foundation of a reliable html seo meta tags generator workflow, ensuring that the final output structure matches exactly what your engineering team needs for the upload.
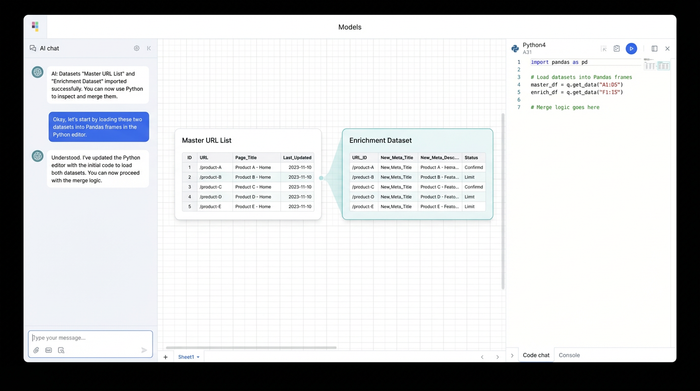
Step 2: Merging data with Python (no more VLOOKUPs)
This is where the workflow shifts from manual labor to data science. In a traditional spreadsheet, you would write a formula like =VLOOKUP(A2, 'New Content'!A:B, 2, FALSE) and drag it down thousands of rows. This consumes processing power and leaves the sheet vulnerable to user error.
In Quadratic, you can use Python to merge these datasets instantly and accurately. Python is native to the grid, meaning you can learn Python with zero knowledge and write a script directly in a cell to process your data. We will use the Pandas library, a standard tool for data analysis, which excels in managing large datasets, to map the new content to the master URLs.
Here is how a simple merge script looks in Quadratic:
import pandas as pd
master_df = cell("A1:C5000")
new_content_df = cell("F1:H5000")
final_df = pd.merge(master_df, new_content_df, on='URL', how='left')
final_df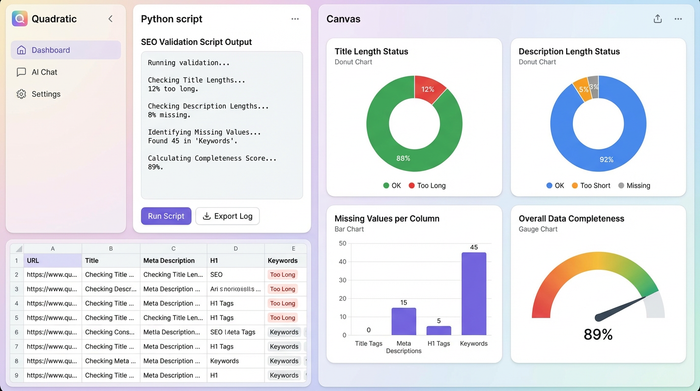
This script systematically locates specific URLs in your master list and fills in the missing meta tag information from your new content list. It guarantees data integrity. If a URL exists in the master list but not in the new content list, Python handles it gracefully without returning error codes that break your export. You have effectively built a custom seo tools meta tag generator specifically tailored to your site's architecture.
Step 3: Visualizing and updating in batches
One of the unique advantages of the Quadratic infinite canvas is the ability to organize your work spatially. Real-world SEO projects are rarely approved all at once. You might have the "Shoes Category" ready for upload while the "Accessories" section is still being drafted.
In a standard spreadsheet, filtering for these specific batches is tedious. In Quadratic, you can output your Python merge results into distinct grids and physically move them around the canvas. You can place your "Shoes" update batch on the left side of your workspace and your "Accessories" batch on the right.
This visual grouping allows you to review and approve batches of metadata independently. You can verify that the H1s align with the Title Tags for a specific category without being distracted by thousands of unrelated rows. Once a batch is approved, it is ready to be exported.
Step 4: Validating character counts and completeness
Before you export your file for the CMS, you must ensure the data adheres to SEO best practices. Search engines truncate titles longer than 60 characters and descriptions longer than 160 characters, aligning with search engine guidelines for snippet length.
You can add a validation step to your Python script or use standard spreadsheet formulas to flag issues. For example, you can create a new column that checks the length of your generated titles and highlights any that exceed the limit.
final_df['Title_Length'] = final_df['New_Title'].str.len()
final_df['Status'] = final_df['Title_Length'].apply(lambda x: 'Too Long' if x > 60 else 'OK')This programmatic approach ensures that your meta tags for seo generator workflow includes quality assurance by default. You can instantly see how many rows are missing values or exceeding character limits, allowing you to fix them before they ever reach the live site.
Conclusion: From spreadsheet to CMS
Managing SEO metadata at scale requires more than just creativity; it requires a rigorous data workflow. By moving from fragile spreadsheet formulas to a Python-enabled environment, you eliminate the risk of mapping errors and gain better visibility into your progress.
The workflow described here—importing raw data, merging data reliably with Python, visually organizing batches on an infinite canvas, and validating the output—turns a chaotic process into a streamlined operation. You are no longer just looking for an seo meta tag generator to write text; you are building a system that generates the final, clean dataset your website relies on.
Start building your own bulk management workflow in Quadratic today and take control of your SEO data.
Use Quadratic to batch update SEO meta tags
- Eliminate fragile VLOOKUPs: Use robust Python scripts directly in the grid for accurate, instant data merges, preventing common spreadsheet errors when mapping new content to URLs.
- Visually organize large projects: Utilize an infinite canvas to place distinct datasets side-by-side and group update batches (e.g., "shoes" vs. "accessories"), enabling clear oversight and independent approval.
- Build crash-proof workflows: Leverage native Python and Pandas to manage thousands of URLs and content pieces reliably, ensuring data integrity without manual cell dragging or formula breakage.
- Automate validation and QA: Embed Python scripts to instantly check meta tag character counts and completeness, flagging issues before export to your CMS.
- Streamline export to CMS: Generate clean, validated datasets tailored to your engineering team's requirements, turning chaotic bulk updates into a controlled, efficient process.
Ready to streamline your SEO data management? Try Quadratic today.