For many accounting teams, the "close" is a source of recurring dread. It is synonymous with late nights, caffeine-fueled scrutiny of transaction logs, and the high-stakes pressure of ensuring every penny is accounted for before the books are locked. The anxiety often stems not from the accounting theory itself, but from the logistical nightmare of the process. You are chasing down missing receipts, wrestling with CSV exports that don't match, and praying that the complex web of spreadsheet formulas doesn't break at the eleventh hour.
The reality for modern controllers and CFOs is that the bottleneck usually isn't the accountant's skill; it is the workflow. As companies scale, the volume of data outpaces the capabilities of traditional, static spreadsheets. Yet, moving to a rigid, expensive Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) module for every reconciliation task is often overkill and lacks the flexibility finance teams need.
This guide covers the essential checklist for a successful close and introduces a modern method to handle the heavy lifting. By shifting your mindset from manual data entry to a data-connected workflow, enabled by spreadsheet automation, you can transform the month end reconciliation process from a chaotic scramble into a streamlined, audit-proof routine.
What is month-end reconciliation?
At its core, month-end reconciliation is the process of verifying that the balances in your General Ledger (GL) align perfectly with external documentation and subledgers. It is the "prove it" phase of the accounting cycle. Before you can issue financial statements to the board or investors, you must validate that the numbers in your accounting software reflect reality.
This involves comparing internal records against bank statements, credit card processing reports, and inventory counts. The goal of this transaction reconciliation is to identify discrepancies—whether they are caused by timing differences, human error, or fraudulent activity—and resolve them before the period is closed.
The stakes are high. Beyond the obvious need for accurate financial reporting, a robust month end account reconciliation process is critical for compliance and audit readiness. When auditors arrive, they don't just want to see the final numbers; they want to see the work. A clean, consistent end of month reconciliation proves that the company has strong internal controls, reducing the risk of restatements and building trust with stakeholders.
The essential month-end checklist
While every business has unique nuances, the foundational steps of the close remain consistent. Following a structured checklist ensures that no account is overlooked in the rush to finalize the books.
- Step 1: Record all transactions
Before you can reconcile, you must ensure the data is complete. This involves posting all supplier invoices, recording customer payments, and ensuring all accruals for the month are booked. If the data isn't in the system, the reconciliation will fail before it begins.
- Step 2: Cash reconciliations
Cash is king, and it is also the most prone to error. This step involves matching the transactions in your cash ledger against the bank statement lines. This is often where teams get stuck on specifics, such as finding Relay end-of-month cash reconciliation support or deciphering bundled deposits from payment processors. You might find yourself asking which card simplifies month-end cash reconciliations by separating expenses clearly, but ultimately, the goal of automated bank reconciliation is to ensure the bank balance and book balance tie out to the penny.
- Step 3: Subledger to GL tie-outs
Your GL is only as good as the details supporting it. You must verify that the Accounts Receivable (AR) aging report matches the AR balance in the GL, a process known as accounts receivable reconciliation, and do the same for Accounts Payable (AP) and Inventory. Discrepancies here often indicate manual journal entries that were posted directly to the control account instead of through the subledger.
- Step 4: Review and adjust
Once the cash and subledgers are tied out, you move to adjusting entries. This includes recording depreciation, amortizing prepaid expenses, and recognizing revenue. This is also the stage for reviewing suspense accounts and clearing them out.
- Step 5: Generate the reporting pack
With the balances verified and adjusted, the final step is compiling the financial statements. This reporting pack is what the CFO and Controller will review to sign off on the month.
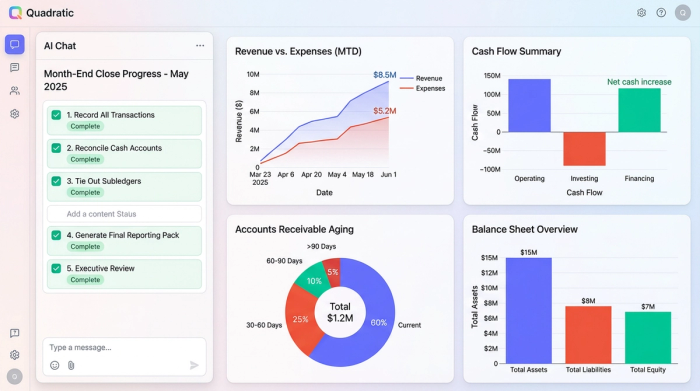
The "data wrangling" gap: why traditional spreadsheets break
If the checklist is so straightforward, why is the process so painful? The answer lies in the "data wrangling" gap. Most accounting guides tell you what to do, but they rarely address how to handle the massive volume of data required to do it.
Accounting teams frequently export massive CSV files from their ERP (like NetSuite, Sage, or QuickBooks) and attempt to manipulate them in traditional spreadsheets. This leads to several critical pain points:
- Manual copy-pasting errors: Every time you manually copy data from a CSV and paste it into a reconciliation workbook, you risk shifting a row, missing a column, or pasting over existing formulas.
- Static, stale data: The moment you export a report, it is dead data. If an adjustment is made in the ERP five minutes later, your spreadsheet is already wrong. You have to repeat the export-and-paste cycle, which is a waste of high-value time.
- Fragility: Traditional spreadsheets rely on cell references (e.g., A1:C500). If next month's report has 600 rows, your VLOOKUPs might miss the new data, or your sum formulas might fall short.
When finance professionals ask, "how do I speed up month-end reconciliation," the answer isn't just "work faster." It is about changing the tool. You need a solution that sits between the raw data and the final report—a connected environment that automates the ingestion and comparison of data without the fragility of manual cell references.
A modern workflow: automating the close in Quadratic
The middle ground between the chaos of Excel and the rigidity of enterprise software is a code-powered spreadsheet. Quadratic offers a canvas where you can combine the familiarity of a spreadsheet grid with the power of Python and SQL. This allows you to build a month-end workflow that is flexible, repeatable, and audit-proof.
By treating the reconciliation process as a data engineering task rather than a data entry task, you can automate the most tedious parts of the close. Here is what a modern workflow looks like in practice, based on real user success stories.
1. Centralizing data streams
In a traditional workflow, a controller might have ten different Excel files open: one for the bank download, one for the credit card processor, one for the GL dump, and so on. In Quadratic, you can centralize these streams into a single, infinite canvas.
Instead of copy-pasting, you can pull data directly into separate sheets within the Quadratic workspace. For example, you can ingest the full General Ledger detail into one sheet and your subledger exports into another. If you are using NetSuite reports, you can bring that raw CSV data into a dedicated "Data - GL" sheet. Similarly, third-party data sources, such as Amazon payout reconciliation month-end data, can live in their own specific sheets.
The benefit here is data sovereignty. The raw data lives in the sheet, but it remains pristine. You aren't touching the source files or risking accidental deletion of a row. You are simply staging the data in a secure, centralized environment where it is ready to be queried.
2. Automating tie-outs with control totals
This is where the magic happens. In a standard spreadsheet, comparing the GL to a subledger involves a web of VLOOKUPs or SUMIFs that drag down performance and break easily. In Quadratic, you can use SQL or Python directly within the sheet to query the raw data you just staged.
Imagine a "Control Total" dashboard at the top of your canvas. Instead of manually checking if the numbers match, you write a simple SQL query that sums the total from your GL sheet and compares it to the sum of your Subledger sheet.
You can program the cell to display a simple "TRUE" or "FALSE," or even use conditional formatting to light up red if there is a variance and green if it ties out. Because you are querying the dataset rather than referencing specific cell ranges, the logic holds up even if the row count changes next month.
When people search for the best software for month-end account reconciliation, they are often looking for a rigid tool that forces them into a specific box. However, the best tool is often a flexible one that you build to fit your specific needs. With Python, you can write scripts that automatically categorize transactions based on descriptions, fuzzy match amounts that are slightly off due to currency conversion, or flag duplicates instantly.
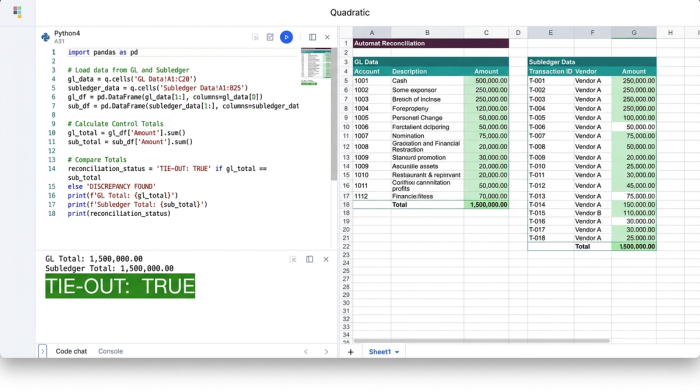
3. Building the status tracker & reconciliation pack
The final piece of the puzzle is visibility. Usually, the "Reconciliation Pack" is a folder full of PDF printouts or a shared drive that is difficult to navigate. In Quadratic, you can build a live, interactive Status Tracker right next to your data.
You can create a master list of all Balance Sheet accounts with a status column (Open, Review, Closed). Because Quadratic allows for Python integration, you can even automate the status. For example, if the Control Total for Cash matches the Bank Statement exactly, the status can automatically flip to "Review."
This dashboard can include dedicated fields for preparer and reviewer initials, timestamps, and, crucially, exception notes. If there is a variance, the accountant can leave a note explaining the timing difference directly in the cell next to the data. This creates a "Reconciliation Pack" that is not a static artifact, but a living document that gives the CFO an instant, high-level view of the close progress without having to email the team for updates.
Why code-powered reconciliation is audit-ready
One of the biggest misconceptions about using code in accounting is that it makes things more complex. In reality, it simplifies the audit process. Auditors value traceability and consistency above all else.
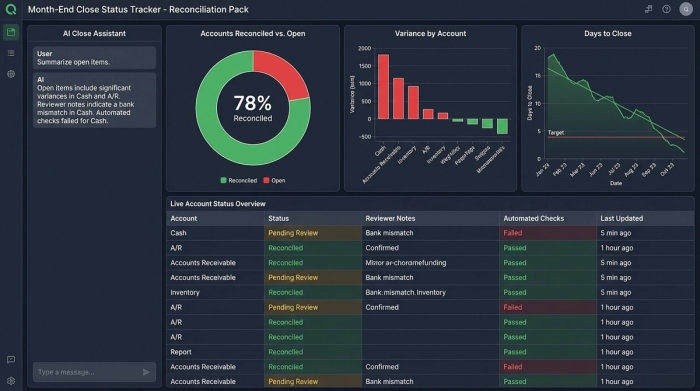
When an auditor looks at a complex Excel workbook, tracing the logic of nested IF statements and cross-sheet references is a nightmare. They often have to ask the controller to "re-perform" the calculation to prove it works.
In a code-powered workflow, the logic is transparent. The auditor can see the SQL query: "SELECT SUM(Amount) FROM General_Ledger WHERE Account = 'Cash'." There is no ambiguity. The logic is readable, and more importantly, it is consistent.
Next month, you don't have to rebuild the wheel. You simply update the data sources—drop in the new CSVs or refresh the connection—and the reconciliation logic runs automatically. This ensures that the process is performed exactly the same way every time, eliminating the variability of human error.
You don't always need complex AI software for month-end account reconciliation to achieve this level of efficiency. Sometimes, you just need Python scripts that reliably categorize transactions and SQL queries that aggregate data accurately. This approach provides the audit trail that modern compliance standards demand while giving the finance team the speed they crave.
Conclusion
Month-end reconciliation doesn't have to be a choice between manual spreadsheet chaos and expensive, rigid software modules. By treating the close as a data engineering problem, you can build a workflow that is both flexible and robust.
Centralizing your data, automating tie-outs with code, and creating a live status tracker allows you to reclaim hours—if not days—from the monthly cycle. It moves the finance team away from the drudgery of data entry and toward the high-value work of analysis and strategy.
If you are tired of broken links and late nights, it is time to try a different approach. Building your first "Reconciliation Pack" in Quadratic can show you the difference between a static spreadsheet and an infinite data canvas designed for the modern era. By leveraging the power of Python and SQL within your familiar grid, you can turn month-end reconciliation into a seamless, automated advantage for your business.
Use Quadratic to do month end reconciliation
- Centralize all reconciliation data: Pull general ledger details, subledger exports, bank statements, and third-party data into a single, infinite canvas, eliminating fragmented files and manual copy-pasting errors.
- Automate tie-outs with code: Use Python or SQL directly in the grid to query raw data, compare control totals, and automatically flag discrepancies, replacing fragile spreadsheet formulas and static data.
- Build live reconciliation dashboards: Create interactive status trackers that update in real-time, providing instant visibility into close progress and replacing static, hard-to-navigate reporting packs.
- Ensure audit readiness and consistency: Leverage transparent, repeatable code logic for every reconciliation, providing clear audit trails and eliminating human error for a consistently audit-proof process.
- Scale your close process flexibly: Adapt your reconciliation workflows to growing data volumes without the rigidity of expensive ERP modules, using a tool that molds to your specific accounting needs.
Ready to streamline your month-end close? Try Quadratic.

